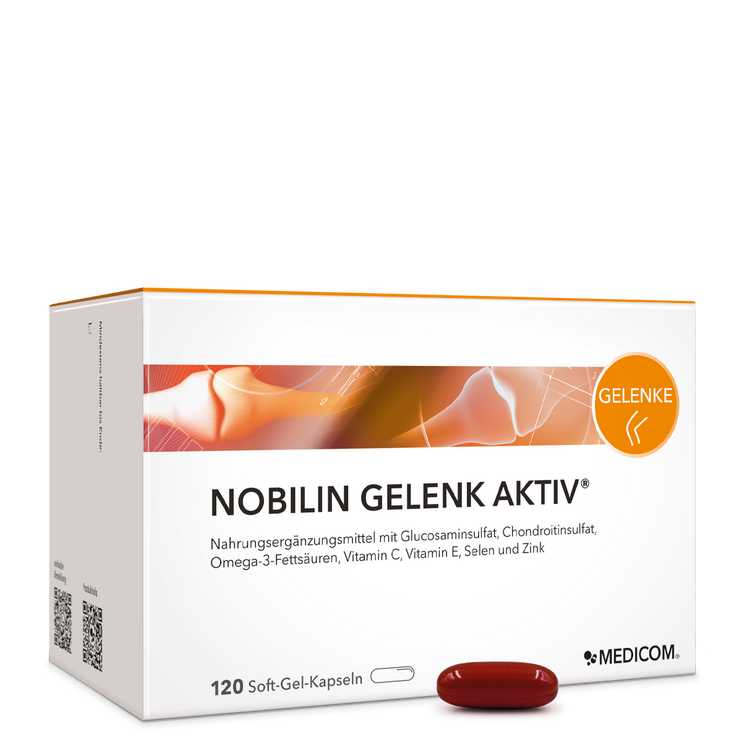
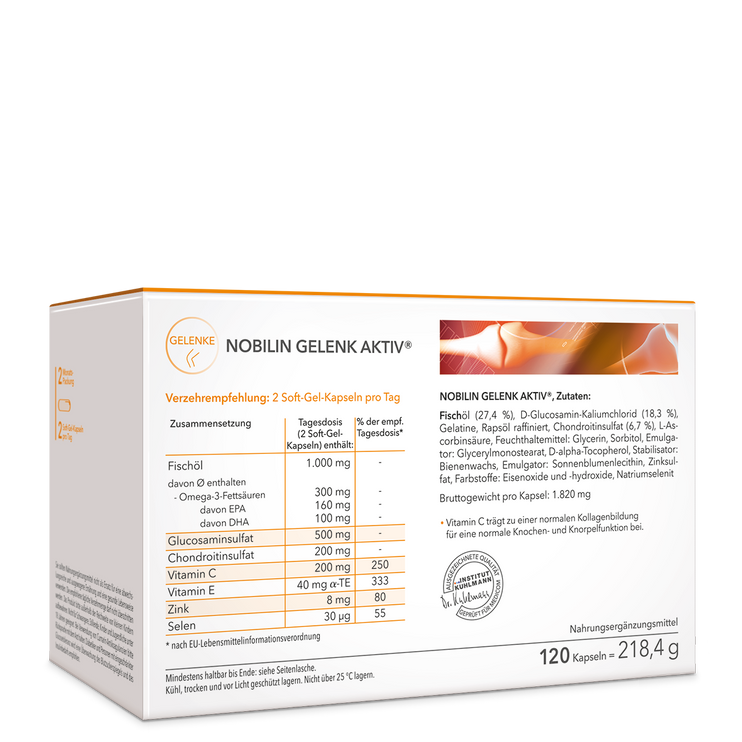
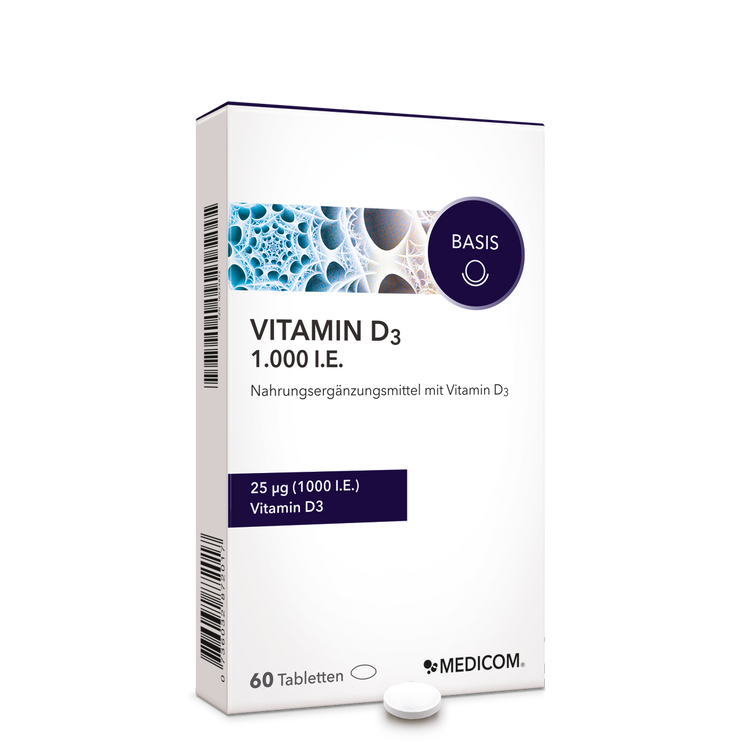
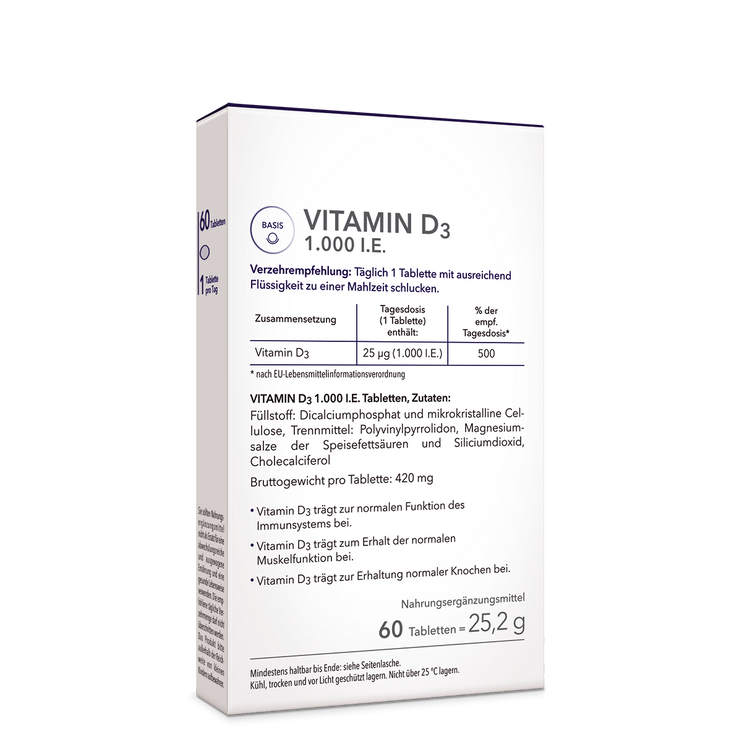
Regardless of whether you are an amateur or a professional athlete: If you really work up a sweat, you have a higher need for nutrients. This starts withmagnesium, which is increasingly sweated out during physical exertion. The need forhigh-quality proteins and fatty acidscan increase, so many athletes swear by nutritional supplements in whichessential amino acids such asL-tryptophanin exact dosage. The semi-essential amino acidL-Arginineenjoys a good reputation among people who do intensive strength or endurance sports. Of the more than 250 known amino acids, 20 are proteinogenic, which means that they serve as building blocks for proteins in the human body.
Antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids
During and shortly after intensive training, short-lived inflammatory reactions occur in the body. Free radicals are also increasingly formed. Therefore, it is particularly important for those who are active in sports toeffective antioxidantsThese include certain carotenoids and theCoenzyme Q10. But alsoOPC(oligomeric proanthocyanidins) fromGrape seed extractandAstaxanthinare excellent “radical scavengers”.
In addition, it is recommended for athletes to consumeOmega-3 fatty acidsNot only because this healthy fat also has an antioxidant effect – it also has positive effects on the muscles, for example byincreased muscle protein synthesissupported. There is also a constant increase in the need for omega-3 fatty acids, particularly in people who are very active in sports.