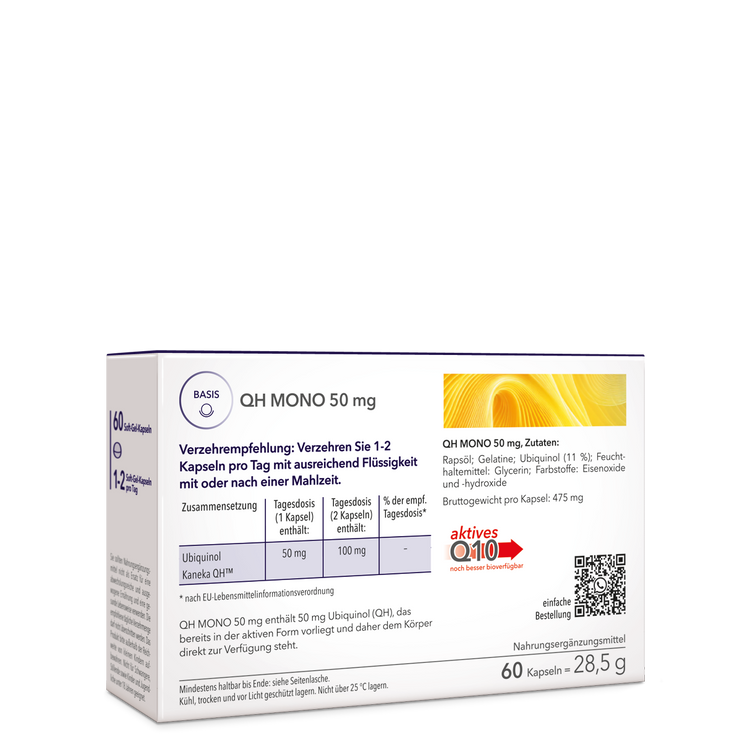
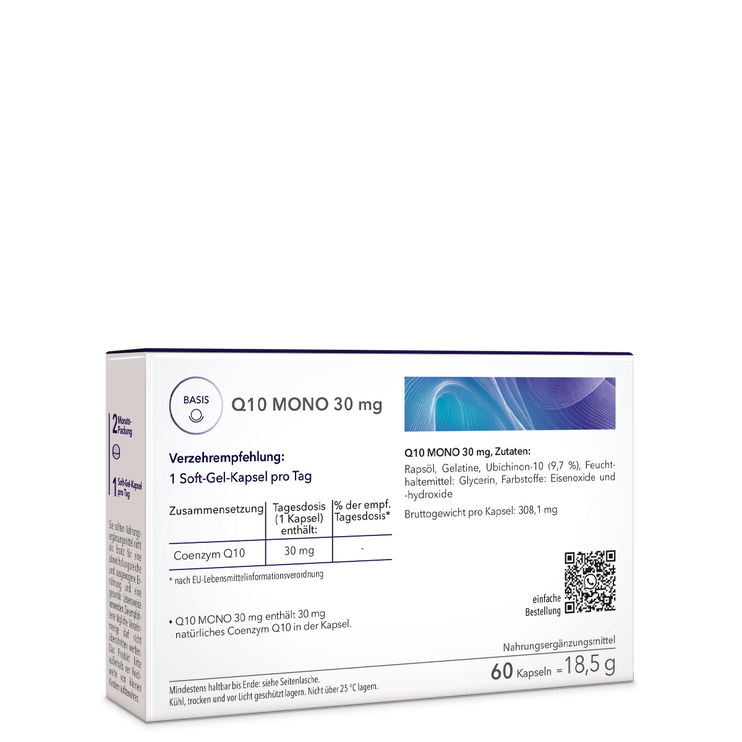
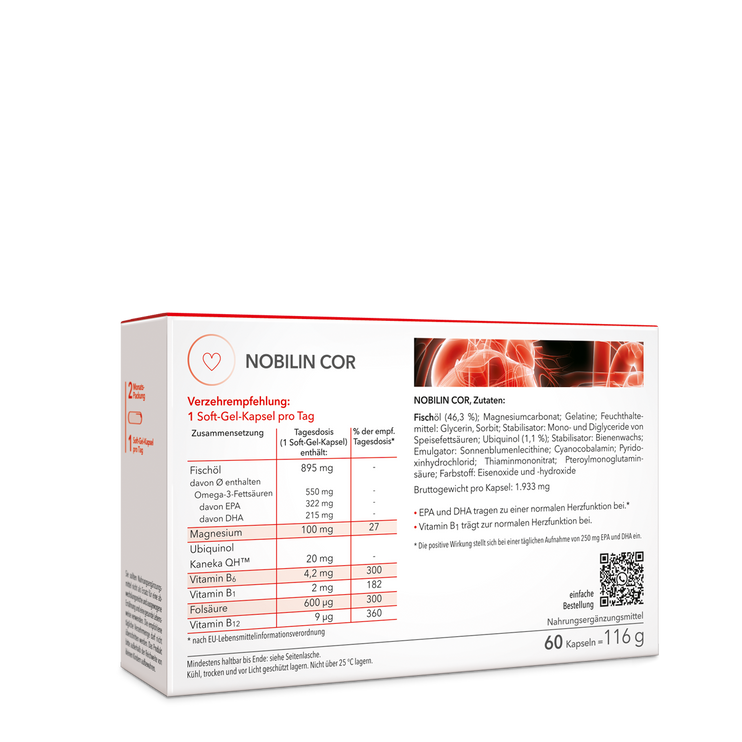
Coenzyme Q10 supports theEnergy production of our cellsand is particularly in connection with Vitamin E andvitamin Can extremelyeffective radical scavenger.
Which foods contain coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 is found in foods such as meat, liver, fish, eggs and vegetable oils.
Origin and function of coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 is also known asUbiquinoneThis name derives from the Latin word“ubiquitous“off, the"everywhere"It illustrates thatCoenzyme Q10in almostall cells of the human bodyThe covitamin is found in theMitochondriaused in the conversion of nutrients into energy. Coenzyme Q10 is an important element in a chain ofMetabolic processes, with which the body makes use of food energy. This process is also known as“Respiratory chain”In addition, coenzyme Q10 fulfils important functions in theCell membraneThe presence of coenzyme Q10 keeps the cell mobile and flexible and enables it to perform its functions better. Functional cell membranes ensure thatMedicinesbe better received, thepain-relieving effect of a medicinal substancetakes effect more quickly and symptoms subside sooner.Coenzyme Q10still has importantantioxidant properties. It eliminatesFree radicalsalready in the cell wall and does not allow them to cause any damage in the cell.
More coenzyme Q10 from the age of 40
The Q-coenzymes come into theVariants Q1 to Q10– but only the higher quality coenzyme Q10 canimmediately in the human metabolismOur organism has the ability to absorb low Q values from food into theto convert higher quality Q10or even from theamino acidsto produce phenylalanine and tyrosine. However, this ability diminishes with age. From the age of40th year of lifeshould therefore be based on asufficient coenzyme Q10 supplybe respected.
Use of coenzyme Q10
Cardiovascular system: Some scientific studies use coenzyme Q10 in heart failure because of its effects on theHeart functionhas.
antioxidant: Coenzyme Q10 is said toantioxidant propertiesand the oxidation ofcholesterolinhibit.
Regeneration of vitamin E: Coenzyme Q10 is involved in the regeneration ofVitamin Einvolved.
Physical stress: Injuries, surgeries and chronic diseases can increase the need forCoenzyme Q10increase.
cholesterol: Coenzyme Q10 is particularly important for patients suffering fromelevated cholesterol levelsand are treated. Statin treatment not only inhibits the body’s own cholesterol synthesis, but also the formation of coenzyme Q10 – aDeficiency of coenzyme Q10is the result. It should be through diet or withNutritional supplementsbe balanced.
Am I lacking coenzyme Q10?
Already ata relevant pointyou should consider additional intake of coenzyme Q10:
- Are youover 40 years old?
- Become a memberStatinstreated?
- Consumerarely meat and sausage products?
- Do you often find yourself understress?
- Are you oftenExposed to pollutants?
How much coenzyme Q10 does the body need?
Independent nutritionists recommend a daily intake of 30 mg of coenzyme Q10.